
This substation, however, is tasked with stepping down the voltage.
DistributionĮventually, the electricity will reach the end of its journey through transmission lines and enter another substation. After the voltage is stepped up, it flows through transmission lines (high voltage power lines) until it reaches its next destination. This lowers the resistance, allowing the energy to travel long distances with minimal losses.

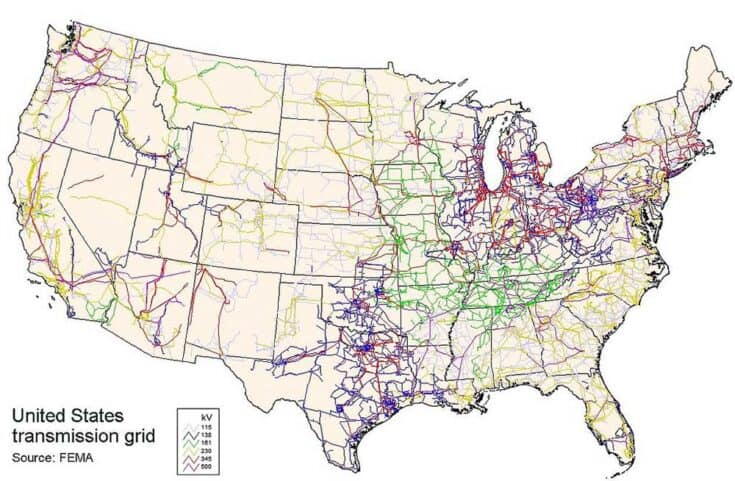
To fix this issue, once the electricity has been generated at a power plant, it travels directly to a step-up substation where it is converted into a higher voltage. TransmissionĮlectricity is carried through wires, which presents a small issue wires create resistance, causing some of that electricity to be lost - and the further the electricity must travel, the more energy we lose. Advances in battery and other storage technologies are being rapidly developed and deployed, clearing a path to a smarter grid. For instance, energy cannot be stored in large quantities the electricity must be created as it is used - barring disaster, the grid is always running. All electricity, regardless of whether it comes from fossil fuels, nuclear, or renewable energy sources, has limitations. The US energy grid is the infrastructure that generates electricity from centralized power plants, transforms it into usable forms, and carries it to us, the consumer. The electricity grid is not yet equipped to handle renewables in the quantity we require, but we can get there with the help of grid mapping software. In fact, the EIA predicts that we will see renewables supply over double what they currently do by 2050 - but it will not be easy. However, renewables have the potential to contribute far more than they currently do.
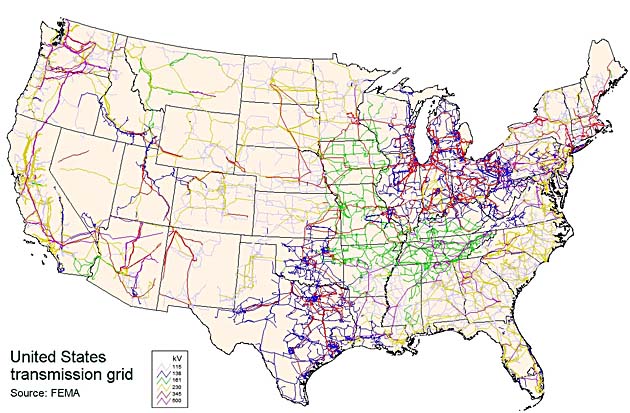
Today, the grid supplies electricity across the nation, powering everything from homes, to factories, to electric cars.Ħ0% of this electricity comes from fossil fuels, 20% from nuclear energy, and 20% from renewable energy sources. In those days, we did not have the slightest of clues what the future of energy looked like, all we knew was that something revolutionary had occurred - and we were right. Late afternoon in lower Manhattan he flipped the switch on the Pearl Street Station’s generators, and thus, the electric grid was born. On September 4th, 1882, Thomas Edison permanently altered history.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
